コンプリート! km michaelis menten equation 122675-Michaelis menten equation km
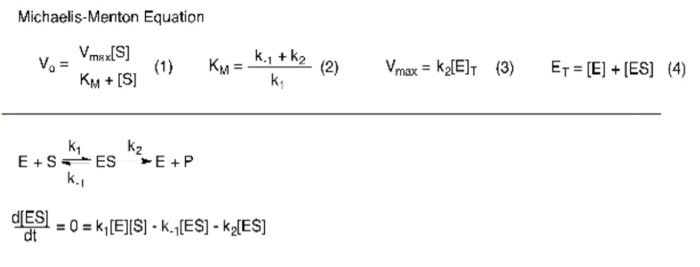
MichaelisMenten equation An equation for evaluating enzyme kinetics in a system v = VS/Km S, where v = Initial velocity of reaction;The equation that defines the MichaelisMenten plot is V = (V max S) ÷ (K M S}) At the point at which K M = S, this equation reduces to V = V max ÷ 2, so K M is equal to the concentration of the substrate when the velocity is half its maximum value Regarding this, what is Vmax and Km?MM equation Vo = Vmax So LB eqn 1/Vo = Km/Vmax(1/So) 1/Vmax Km So 9 How does the MichaelisMenten equation explain why the rate of an enzymecatalyzed reaction is proportional to the amount of enzyme?

Enzyme Kinetics Given Km Find Substrate Concentration At A Certain Velocity Chemistry Stack Exchange
Michaelis menten equation km
Michaelis menten equation km- How to make a michaelis menten graph?S = Substrate concentration Km = Michaelis constant Although Km values are more or less constants for particular enzymesubstrate systems, but these may vary slightly with pH, temperature, ionic strength and also with types and amount of




Michaelis Menten
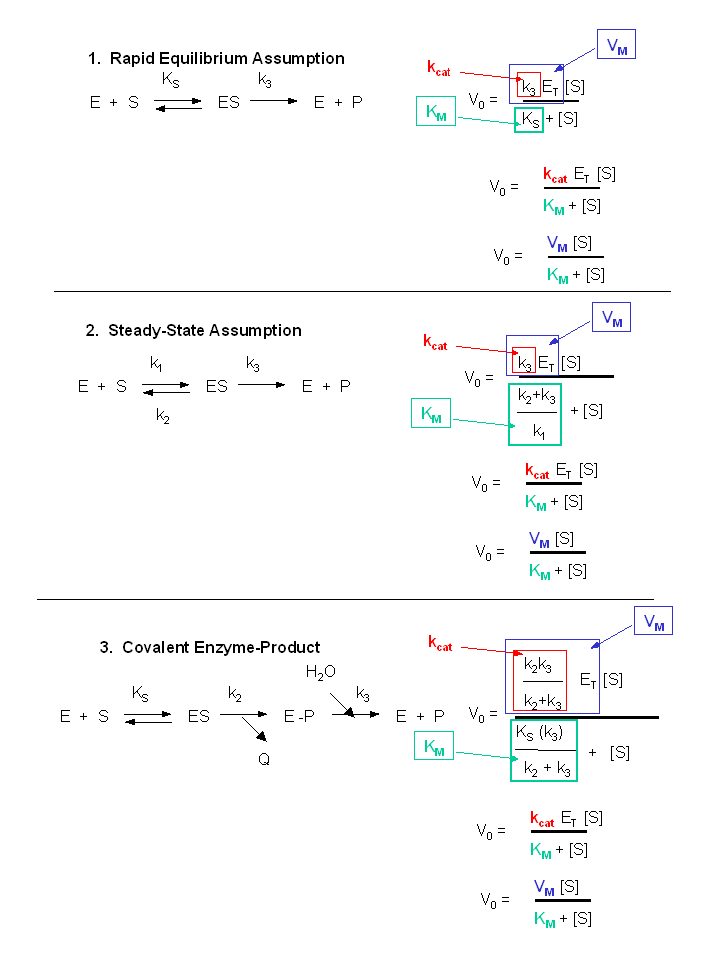
In biochemistry, Michaelis–Menten kinetics is one of the bestknown models of enzyme kinetics It is named after German biochemist Leonor Michaelis and Canadian physician Maud Menten The model takes the form of an equation describing the rate of enzymatic reactions, by relating reaction rate v {\displaystyle v} to {\displaystyle }, the concentration of a substrate S Its formula is given by v =In this case the equation I5 leads to the traditional MichaelisMenten equation, which predicts the initial turnover rate of the enzymatic reaction vo as a function of initial substrate concentration So v S v = max o I6 o K S m o where the constant Km = (k1k2)/kl is called the Michaelis constant and vmax = k2Eo is the maximum turnThe bestfit values of the Michaelis constant (Km) and the maximum velocity (V) in the MichaelisMenten equation can be obtained by the method of least squares with the Taylor expansion for the sum of squares of the absolute residual, ie, the difference
Fitting the MichaelisMenten Equation in MATLAB Disclaimer The goal of this example is to walk you through how to conduct a nonlinear t in MATLAB and compare the results between a nonlinear t and linear t for a given data setK two times ET instead of times ES would be equal to Vmax instead of being equal to Vo like you see at the top I'll make some room here and then sub in K two ES for Vo and K two E total for Vmax and then we finally get to our end equation which is called the MichaelisMenten Equation and is super important when we talk about enzyme kineticsIn enzyme kinetics, Michaelis–Menten equation is a mathematical equation that relates velocity of enzyme V0, maximum velocity Vmax and Km It explains both,
V = Maximum (or limiting) velocity;Michaelis Menten equation can be used to calculate initial velocity of the enzyme, maximum velocity Vmax and Km of an enzyme In this video I explain how toThe Michaelis–Menten equation (Eqn (4)) is the rate equation for a onesubstrate enzymecatalyzed reaction This equation relates the initial reaction rate (v0), the maximum reaction rate (Vmax), and the initial substrate concentration S through the Michaelis constant KM—a measure of the substratebinding affinity




Solved Description The Michaelis Menten Equation Equation Shown Below Gives Us Way Of Quantifying The Effects That Changes In Substrate Concentration Have Over The Overall Rate Of Reaction For An Enzyme Instructions For This




Enzyme Kinetics Michaelis Menten Equation The Bumbling Biochemist
Using graph paper, draw an x and yaxis Label the xaxis mM of S or concentration of substrate Label the y ax sec/micromole of V or velocity of reaction Insert different values of S into the MichaelisMenten equation, along with the values found for Km and Vmax, to solve for V Km is a measure of the affinity an enzyme has for its substrate, as the lower the value of Km, the more efficient the enzyme is at carrying out its function at a lower substrate concentration The MichaelisMenten equation for the reaction above isModel associated with the Michaelis Menten equation is 𝑉𝑉= C(Vmax) C Km 𝜀𝜀 where ε represents normally distributed errors with zero mean and constant variance 𝜎𝜎2 It provides estimates, confidence intervals, and statistical hypothesis tests based on this assumption The method is documented in the
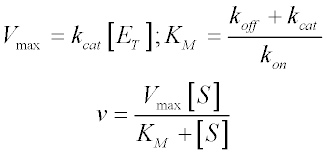



Michaelis Menten Kinetics And Briggs Haldane Kinetics



Kinetics
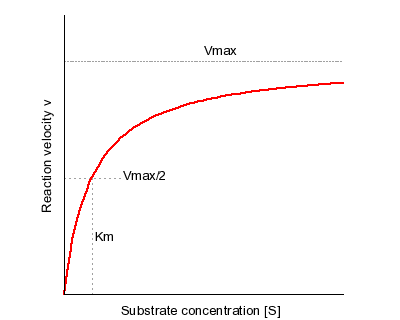
Additionally, how do you solve for KM?MichaelisMenten equation The ratio of kcat to K m can be used to describe an enzyme's catalytic efficiency We also note that kcat Km =k1 k2 k−1 k2 k 1 is the on rate for binding The efficiency of catalysis cannot be greater than the "efficiency" of collisions k 2 / (k1 k 2) describes the fraction of all encounters between EThe MichaelisMenten constant (Km) is an important kinetic parameter for multiple reasons KM is the concentration of the substrate to which the reaction rate is half of the maximum speed Indeed, if KM = S, the MichaelisMenten equation reduces to v = V max / 2




4 Basic Concepts Of Michaelis Menten Kinetics The Michaelis Menten Equation Is Expression Of The Relationship Between The Homeworklib



Add Your Page Title
Substrate concentrations and fitting data to the MichaelisMenten equation Back for decades, linearizations (eg the LineweaverBurk linearization 4, reported years after the MichaelisMenten paper) were instrumental for parameter determination As commented elsewhere 5, the EadieHofstee linearization introduces much lessThe MichaelisMenten equation can be expressed as The velocity is therefore proportional to the enzyme concentration , not inversely so is also referred to as the turnover number As the substrate concentration keeps increasing, then we end up with a steady state in which all the enzyme is boundIn the MM equation above Vmax = k 2Eo In the experiment of Vo vs Eo, So is held constant so all other terms, So, Km, are constant



Michaelis Menten Kinetics And Briggs Haldane Kinetics



Solved Description The Michaelis Menten Equation Equation Chegg Com
M, K m is negligible, and the equation simplifies to) ˇ˙˝ ˛T ˜ˇ˙˝ = ET S S = ET Substituting V max in to the rate equation gives the MichaelisMenten equation !" =!Transcribed image text The MichaelisMenten equation models the hyperbolic relationship between (S) and the initial reaction rate V, for an enzymecatalyzed, singlesubstrate reaction ES=ES EP The model can be more readily understood when comparing three conditions S > Km Match each statement with the condition that it describesThe MichaelisMenten equation has been found to be applicable to a great many enzymecatalysed reactions, and the constants V max and k m determined V max varies with the total concentration of enzyme present, but k m is independent of enzyme concentration and is characteristic of the system being investigated
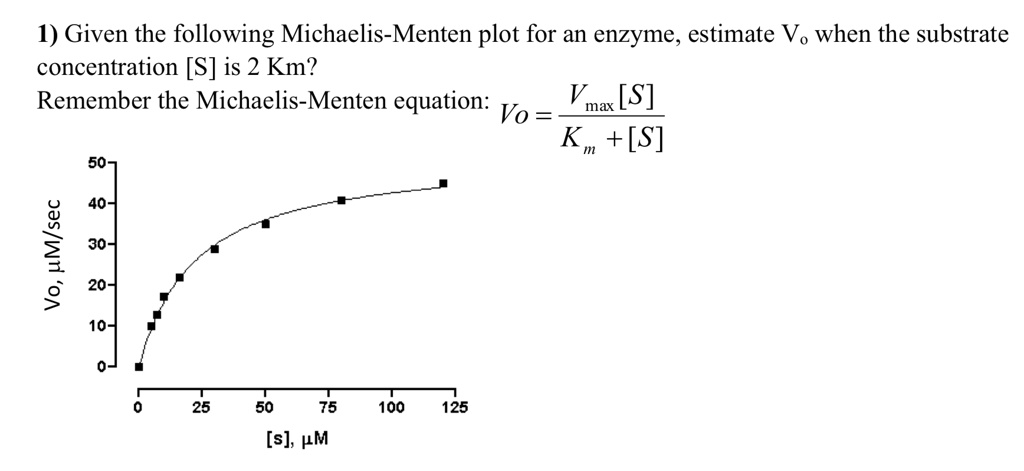



Solved 1 Given The Following Michaelis Menten Plot For An Enzyme Estimate Vo When The Substrate Concentration S Is 2 Km Remember The Michaelis Menten Equation Vmax S Vo K S 50 40 1 30




Solved 9 Applying The Michaelis Menten Equation I An Enzyme Chegg Com
And Km = Michaelis constantMichaelisMenten Equation (Eq 1), S v = V max _____ Eq 1 Km S where v = reaction rate, S = substrate concentration, V max = maximal velocity, and K m is the Michaelis constant Each enzyme has physical characteristics with regard to substrate specificity, reaction velocity or required cofactors that affect the MichaelisMenten constantsVmax is equal to the product of the catalyst rate constant (kcat) and the concentration of the enzyme The MichaelisMenten equation can then be rewritten as V= Kcat Enzyme S / (Km S) Km is the concentration of substrates when the reaction reaches half of Vmax




Michaelis Menten Equation Flashcards Quizlet




Developing A Three Dimensional Animation For Deeper Molecular Understanding Of Michaelis Menten Enzyme Kinetics Florjanczyk 18 Biochemistry And Molecular Biology Education Wiley Online Library
The MichaelisMenten equation has been used to predict the rate of product formation in enzymatic reactions for more than a century As substrate concentrations increase, a tipping point can be reached where an increase in the unbinding rate results in an increase, rather than a decrease, of the reaction rate#$ SSS SSSS ES ES EP k1 Catalysis k 2 k2 Binding k 1 ES EP = ˇ˙˝ S ˘ˇS The MichaelisMenten equation can then be rewritten as V= Kcat Enzyme S / (Km S) Kcat is equal to K2, and it measures the number of substrate molecules "turned over" by enzyme per second The unit of Kcat is in 1/sec Km is the concentration of substrates when the reaction reaches half of Vmax
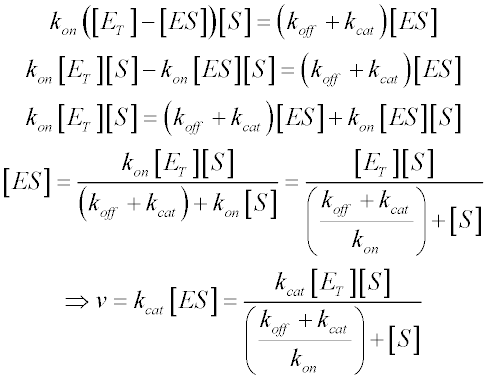



Michaelis Menten Kinetics And Briggs Haldane Kinetics



How Is Michaelis Constant Inversely Proportional To The Affinity Of A Substrate Quora
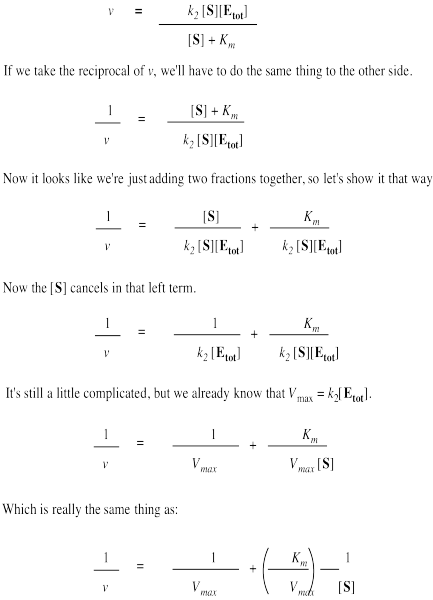
• The MichaelisMenten equation describes the kinetic behavior of many enzymes • This equation is based upon the following reaction S → P k 1 k 2 E S ↔ ES → E P k1 k 1, k1 and k 3 are rate constants for each step To derive the equation, they made 2 assumptions 1 The reverse reaction (P → S) is not considered because theY = Vmax*X/(Km X) Interpret the parameters Vmax is the maximum enzyme velocity in the same units as Y It is the velocity of the enzyme extrapolated to very high concentrations of substrate, so its value is almost always higher than any velocity measured in your experiment Km is the MichaelisMenten constant, in the same units as X It is the substrate concentration needed toA single equation for the velocity of the reaction, V = dS/dt † V = dS dt = VmaxS Km S (12) where † Vmax = k2ETotal Km = k1 k2 k1 The function V = Vmax!S Km!!S is the MichaelisMenten hyperbola Km is the value of S when the velocity of the reaction is half its maximum, Vmax, and the slope of the V(S) curve is Vmax/Km Exercise




Kinetic Analysis Michaelis Menten Equation




Enzyme Kinetics Given Km Find Substrate Concentration At A Certain Velocity Chemistry Stack Exchange
The relationship is defined by the MichaelisMenten equation v = Vmax / (1 (Km/S)) I t is difficult to fit the best hyperbola through the experimental points, and difficult to determine Vmax with any precision by estimating the limit of the hyperbola at infinite substrate concentrationS = Substrate concentration;Rewritten into the familiar form of the MichaelisMenten equation (eq 14) S S m max K V v (14) Next, we imagine what happens when Km > > S as follows in eq 15 S S m max k K V v (15) Since k = Vmax/ Km in eq 15, we refer to Vmax/ Km as




Kinetic Parameters Using Michaelis Menten Equation V Max 1 060 28 Download Scientific Diagram




Michaelis Menten Equation Derivation And Interpretation Youtube
If you have any query regarding video you can mail me on gatebiotechnology22@gmailcomTelegram Channel link https//tme/gbsvGATE22IIT KGP https//gaThe Michaelis equation permits the study and several conclusions about the enzyme characteristics such as (1) initial velocity, (2) Km, and (3) ___ velocity maximal The initial velocity is an important characteristic of the enzyme reactionEquation (11), the MichaelisMenten equation, describes the kinetic behavior of an enzyme that acts according to the simple model (1) Equation (11) is of the form y = ax/(b x) (does this look familiar?) This is the equation of a rectangular hyperbola, just like the saturation equation for the binding of dioxygen to myoglobin
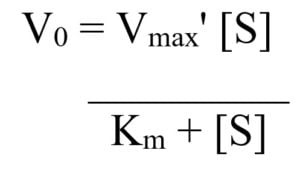



The Michaelis Menten Model Biochemistry Microbe Notes




How To Calculate Enzyme Km Using Michaelis Menten Equation Youtube
The Michaelis Menten kinetic equation is used for determining the kinetics of enzymecontrolled reactions, where the biochemical reaction is assumed to be involving a single substrate MichaelisMenten kinetics allows the computing of the rate of the reaction (V 0 ), substrate concentration S, Michaelis constant (K m ), and the maximum rateHow does the MichaelisMenten equation explain why the rate of an enzymecatalyzed reaction is proportional to the amount of enzyme? The MichaelisMenten Plot The velocity of an enzymecatalyzed reaction is a function of substrate concentration To derive a plot for a particular reaction, researchers prepare several samples of substrate at different concentrations and record the rate of product formation for each sample




Integrated Form Of Michaelis Menten Equation Download Scientific Diagram



2
MichaelisMenten equation Interactive graph The interactive graph provided below allows for a good understanding of the MichaelisMenten equation, how the reaction velocity changes as a function of the substrate concentration, and how changes in Vmax and Km alter the shape of the graph Enter appropriate numerical values for the Maximum The Michaelis constant (Km) and the MichaelisMenten equation The MichaelisMenten equation is the most widely known model in enzyme kinetics Where v0 is the initial reaction rate, S is the substrate concentration, Km is the Michaelis constant, and Vmax is the maximum reaction rate The Michaelis constant describes the kinetics of substrate/enzyme bindingThe MichaelisMenten equation forthis system is Here, Vmaxrepresents the maximum velocity achieved by the system, at maximum (saturating)substrate concentrations KM(the Michaelis constant;sometimes represented as KSinstead) is the substrateconcentration at which the reaction velocity is 50% of the Vmax




Biology Notes For A Level 21 Michaelis Menten Equation And Immobilising An Enzyme




322 h Exp 7 The Effect Of Substrate
The Michaelis–Menten equation (Eqn (4)) is the rate equation for a onesubstrate enzymecatalyzed reaction This equation relates the initial reaction rate (v0), the maximum reaction rate (Vmax), and the initial substrate concentration S through the Michaelis constant KM—a measure of the substratebinding affinity 4 Michaelis Menten hypothesis • Invention Michaelis and Menten , 1913 • Basis According to this mechanism, an enzyme–substrate complex is formed in the first step and either the substrate is released unchanged or after modification to form products 4 5In the MM equation above Vmax = k2Eo In the experiment of Vo vs Eo, So is held constant so all other terms, So, Km, are constant So Vo = constant Eo or Vo is proportional to Eo
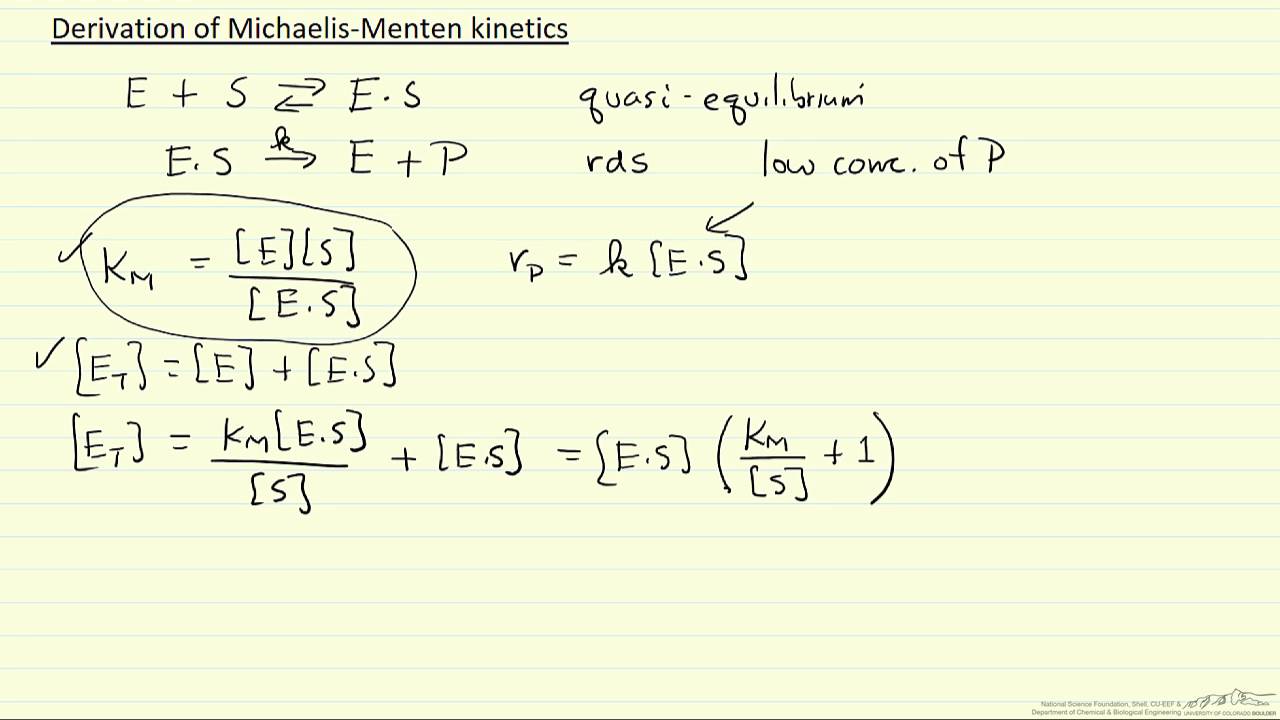



Derivation Of Michaelis Menten Kinetics Youtube
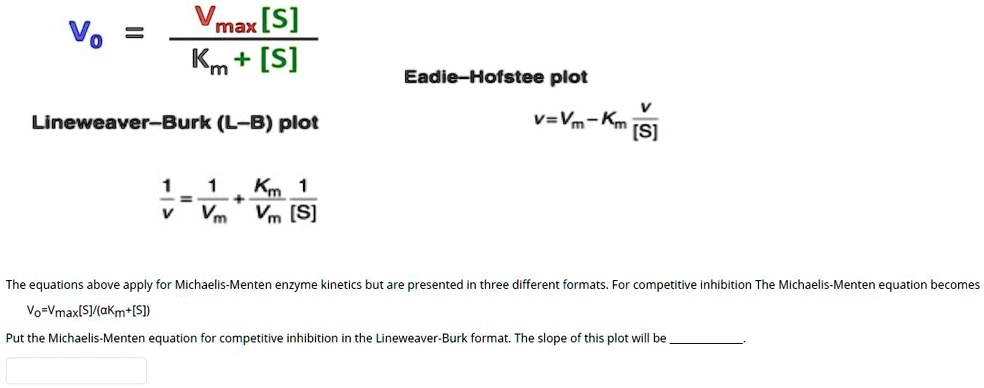



Solved Vmax S Km S Vo Eadie Hotstee Plot Lineweaver Burk L B Plot V Va Kn S 1 Vt Km 1 Vm S The Equations Above Apply For Michaelis Menten Enzyme Klnetics But Are Presented In
K m Michaelis menten equation is used for determining rates of enzyme controlled reactions In the MichaelisMenten equation v denotes the rate of the reaction, v max denotes the maximum rate that was achieved by the system, S denotes the Substrate concentration and K m denotes the Michaelis Constant The Michaelis constant (K m) is equal to the substrate concentration at




Example Data Demonstrating Calculation Of Michaelis Menten Constant K Download Scientific Diagram



1




Michaelis Menten



4 2a Derivation Of The Michaelis Menten Equation Chad S Prep




Michaelis Menten Equation Example 2 Youtube




4 The Double Reciprocal Transformation Of The Michaelis Menten Equation Also Called The Lineweaver Burk Plot Is Give Homeworklib




Michaelis Menten Equation Youtube




Michaelis Menten




Ii Protein Biochemistry 2 6 Enzyme Kinetics 2
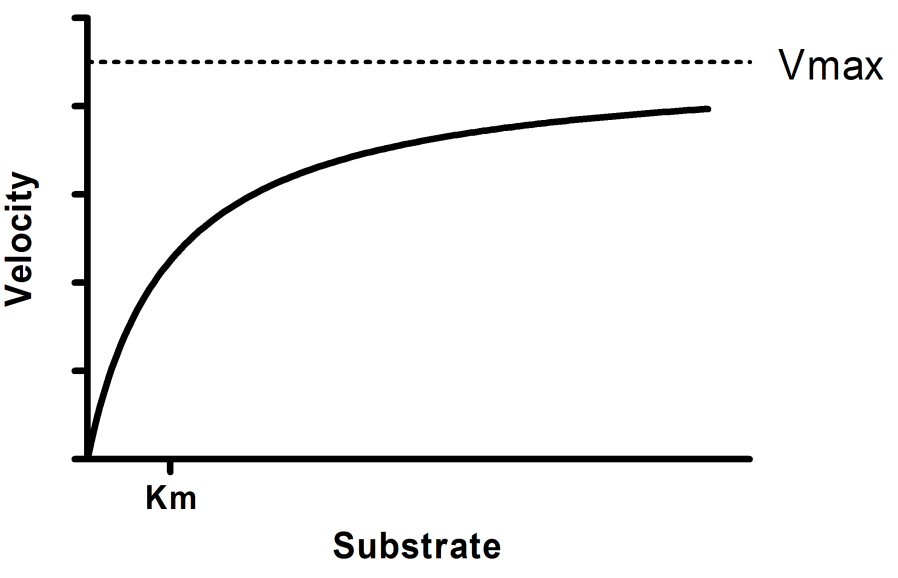



Graphpad Prism 9 Curve Fitting Guide Equation Michaelis Menten Model



2




Solved Derivation Of Michaelis Menten Yields B C Maximal Chegg Com




Michaelis Menten Kinetics Wikipedia




Solved 4 A Modified Michaelis Menten Equation Can Be Chegg Com




Rmax And Km 26 4 Constants From Michaelis Menten Equation Give Insight Into Qualitative And Quantitative Aspects Of Enzyme Kinetics Indicate If Enzyme Ppt Video Online Download



1




Lineweaver Burk Plot Wikipedia




Rectangular Hyperbola Plot Of The Michaelis Menten Equation Relating Download Scientific Diagram




Biochem 1 Flashcards Quizlet
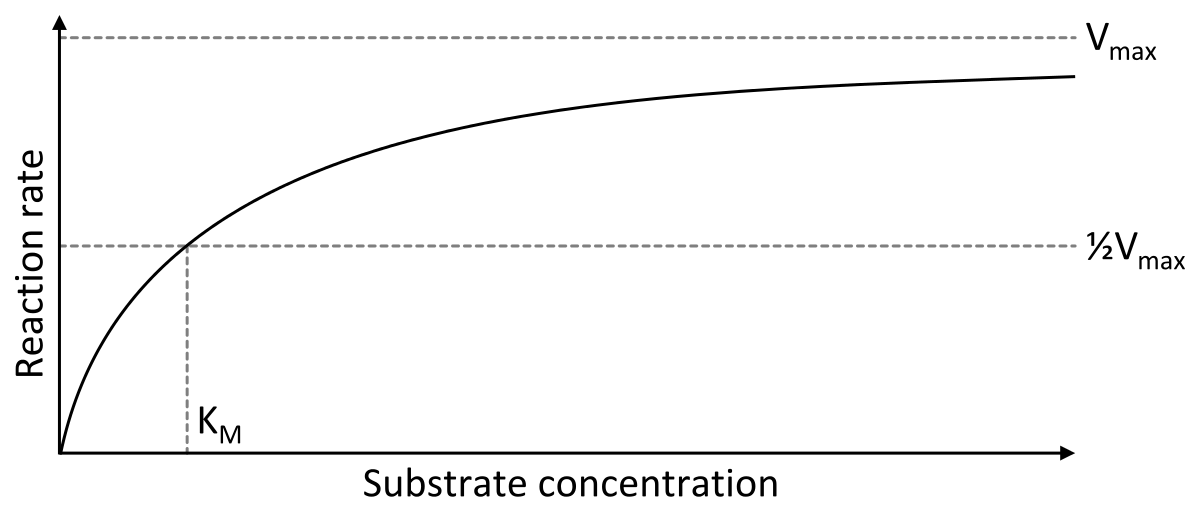



Michaelis Menten Kinetics Wikipedia




Team Astws China Model Igem Org



The Michaelis Menten Equation In Biochemistry Tuition Tube
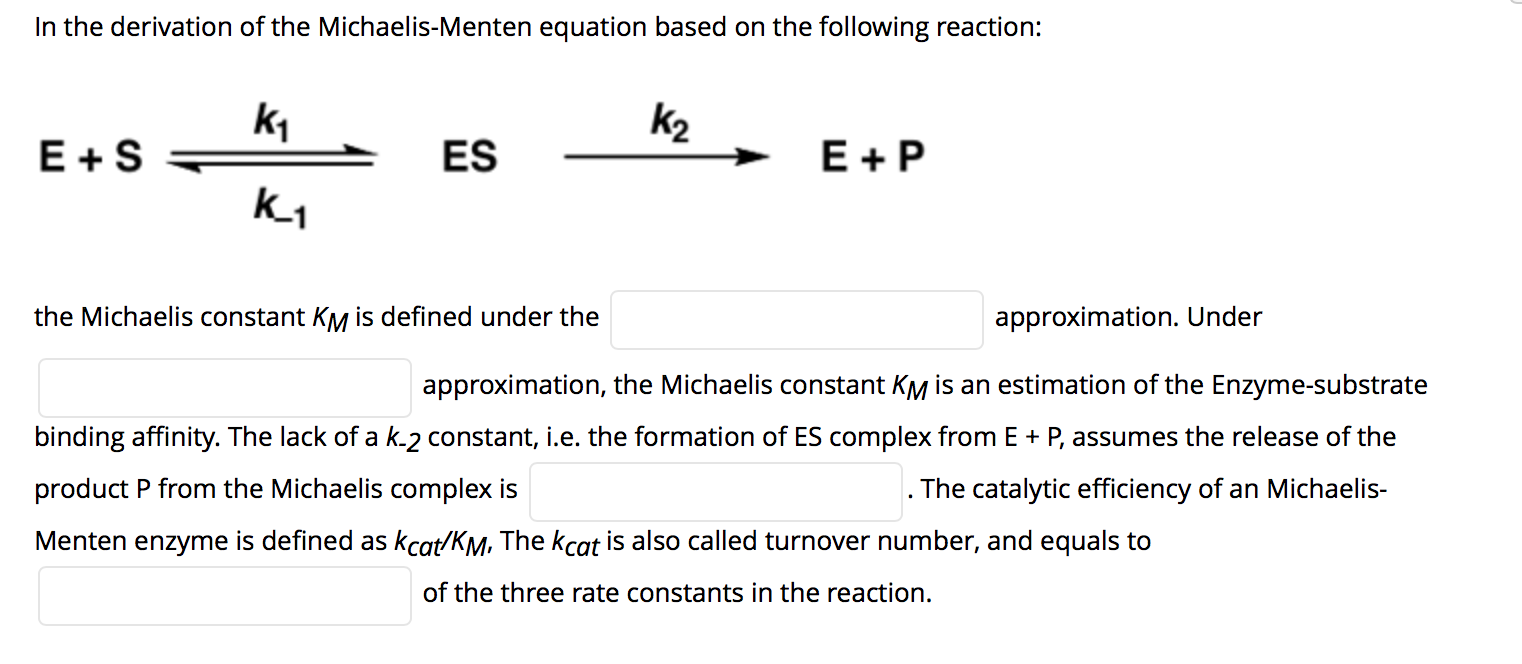



Solved In The Derivation Of The Michaelis Menten Equation Chegg Com




Solved Given The Michaelis Menten Equation Select The Chegg Com




044 Michaelis Menten Equation Youtube




Michaelis Menten Rlc Steve 313 Campbell hm313 Michaelis Menten Equation The Ratio Of Kcat To K M Can Be Used To Describe An Enzyme S Estimation Of Vmax And K M From A Direct Pdf Document
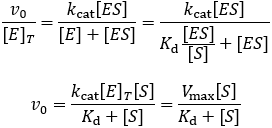



Km Vs Kd The Difference Between Michaelis And Dissociation Constants The Science Snail
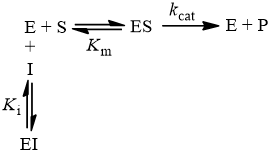



Blog Archives The Science Snail
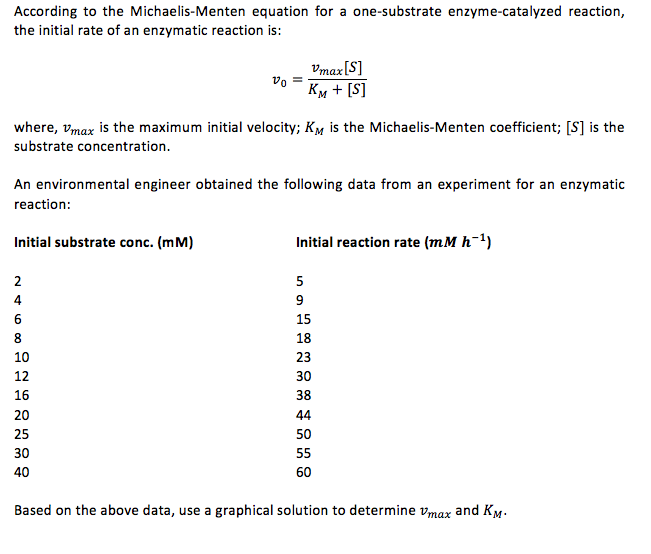



Solved According To The Michaelis Menten Equation For A Chegg Com




Structural Biochemistry Enzyme Michaelis And Menten Equation Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World




Kinetics Control Of Enzyme Activity Mcat Content




Enzyme Kinetics Michaelis Menten Equation The Bumbling Biochemist



1




Enzyme Kinetics Michaelis Menten Equation The Bumbling Biochemist



Chem 440 Special Topic



2




Kinetic Analysis Michaelis Menten Equation



Michaelis Menten Equation Calculator Calistry




Michaelis Menten Equation Biochemistry Enzyme Kinetics Science Resources




Michaelis Menten Kinetics Wikipedia
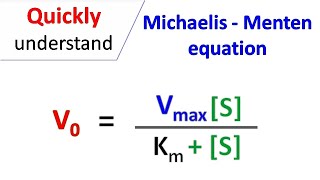



Michaelis Menten Equation Youtube




Biochem Chapter 8 Flashcards Quizlet



Chem 440 Special Topic



2
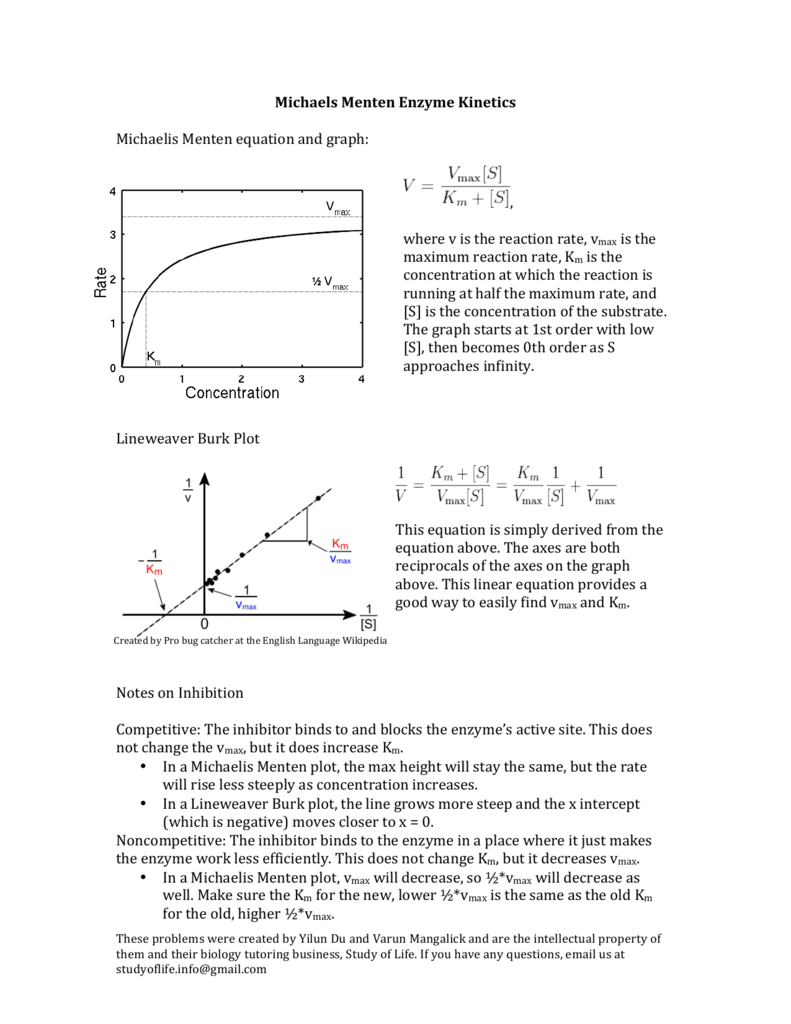



Michaels Menten Enzyme Kinetics Michaelis Menten



What Is The Behavior Of Enzymes By The Michaelis Menten Equation Quora



1
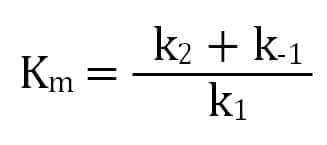



A Quick Primer On Enzyme Kinetics



Rational Function Applications Exercises




Solved According To The Michaelis Menten Equation What Is Chegg Com
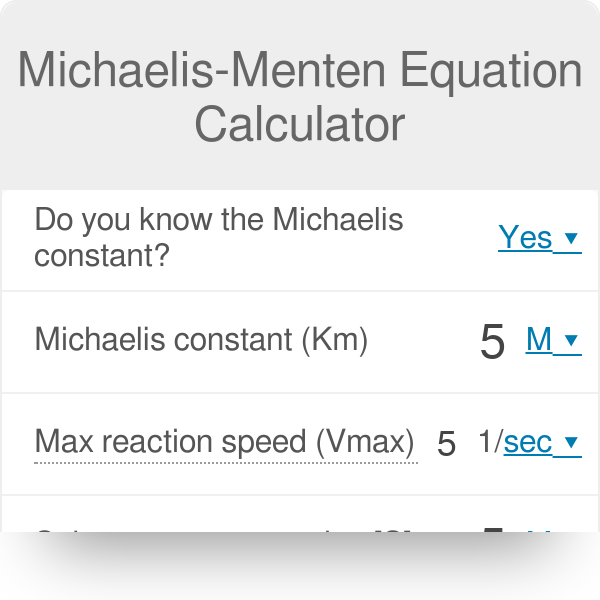



Michaelis Menten Equation Calculator




Hanes Woolf Plot To Identify Km And Vmax Which Were Used In The Download Scientific Diagram



Solved Description The Michaelis Menten Equation Equation 1 Shown Below Gives Us A Way Of Quantifying The Effects That Changes In Substrate Conc Course Hero




Biochemistry I Michaelis Menten Problem 2 Youtube




Enzyme Kinetics Michaelis Menten Equation The Bumbling Biochemist
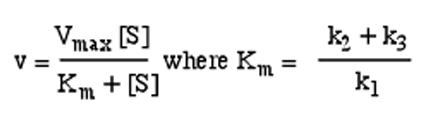



Solved Consider The Michaelis Menten Equation Under What Chegg Com
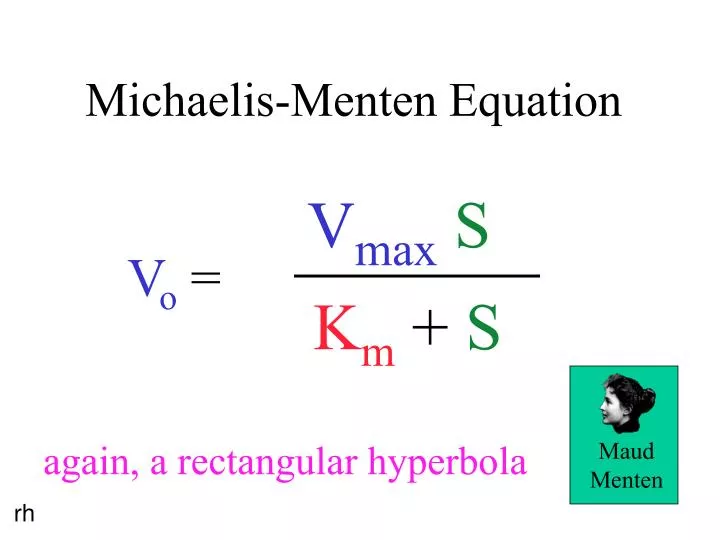



Ppt Michaelis Menten Equation Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 121




Michaelis Menten Explained And Derived Youtube




Michaelis Menten Equation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



2




Lineweaver Burk Plot Wikipedia




Lecture 15 Enzymology Today Howard Salis 148 Baker 3pm Extra Credit Seminar Assignments Due Monday Ppt Video Online Download



2
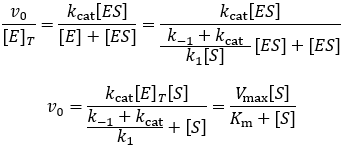



Km Vs Kd The Difference Between Michaelis And Dissociation Constants The Science Snail




The Michaelis Menten Equation Kcat Km




Michaelis Menten Plot Estimating Km Youtube
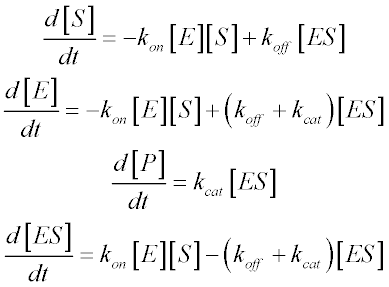



Michaelis Menten Kinetics And Briggs Haldane Kinetics




Structural Biochemistry Enzyme Michaelis And Menten Equation Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World




Kinetic Analysis Michaelis Menten Equation
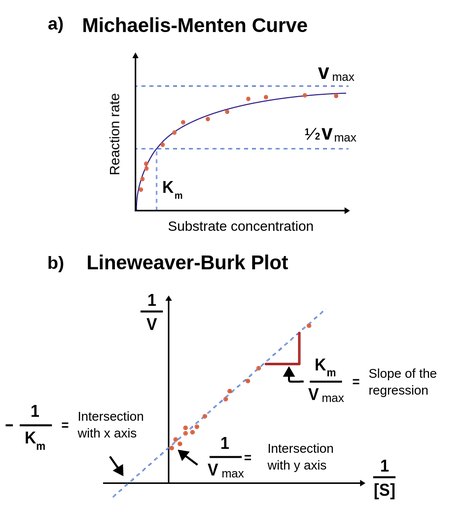



Km Labster Theory




Help Online Origin Help Michaelismenten
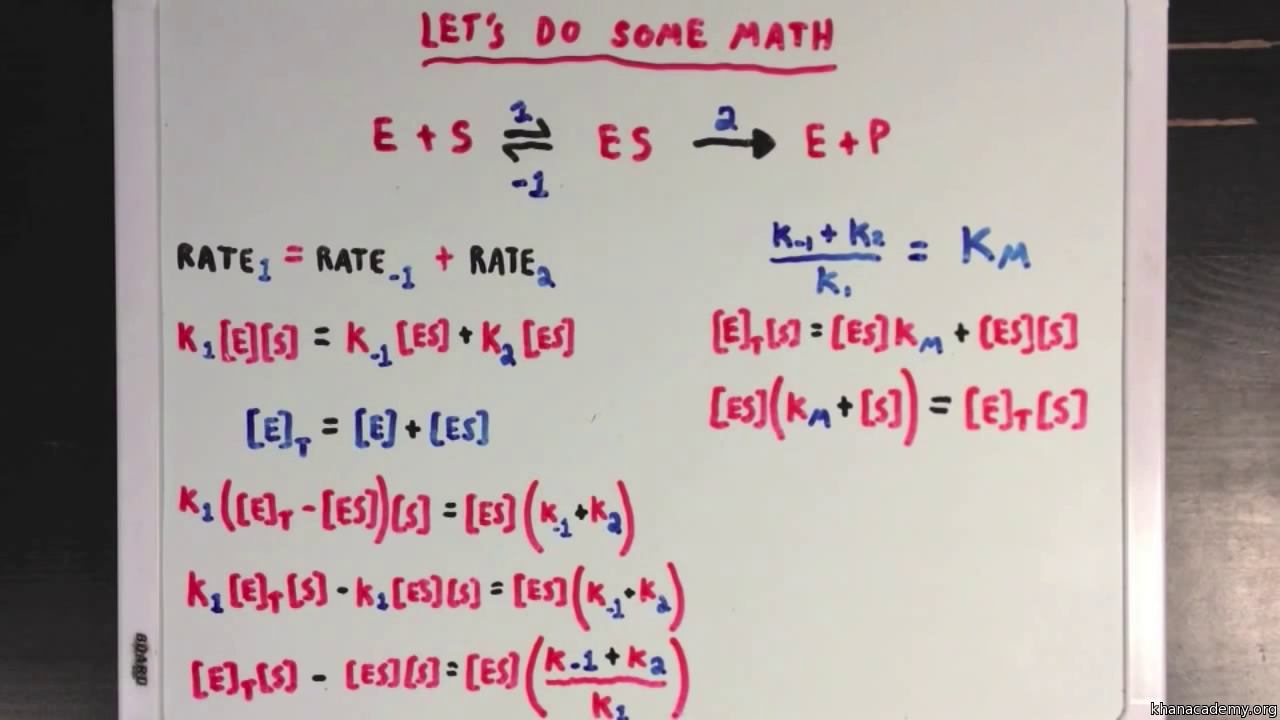



Steady States And The Michaelis Menten Equation Video Khan Academy



Structural Biochemistry Enzyme Michaelis And Menten Equation Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World
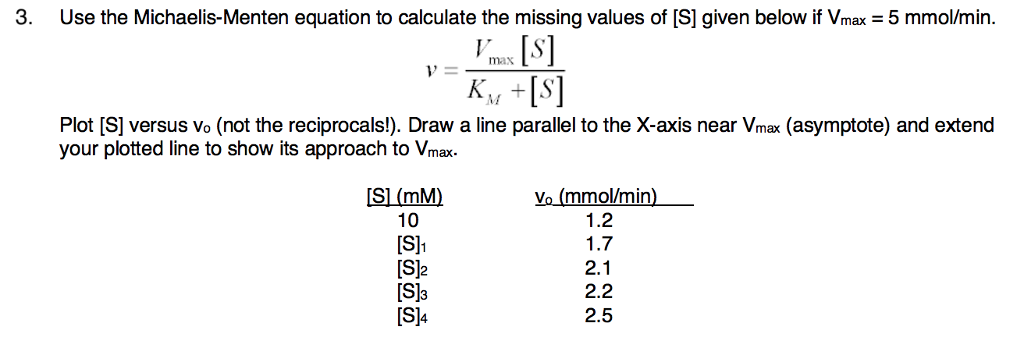



Solved 3 Use The Michaelis Menten Equation To Calculate The Chegg Com




Michaelis Menten Kinetics Ppt Video Online Download




Michaelis Menten Equation Biolympiads




Lesson 6 Michaelis Menten Kinetics Objective




Derivation Of Michaelis Menten Equation Youtube
コメント
コメントを投稿